Conditions
-
 Eye Glossary
Eye GlossaryAdie's Pupil - a pupil that does not react normally to bright light due to impaired nerve function; usually does not interfere substantially with vision
-
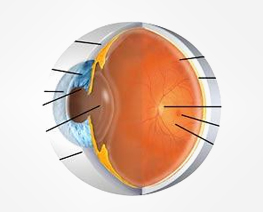 Eye Anatomy
Eye AnatomyThe cornea is the clear, transparent front layer of the eye through which light passes The iris gives our eyes colour and it functions like the aperture on a camera
-
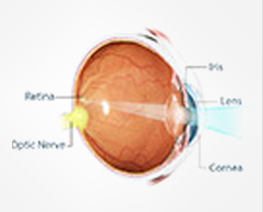 How the Eye Works
How the Eye WorksNormal vision relies on healthy eyes, normal visual pathways and a healthy visual area of the brain.
-
 Vision Disorders
Vision DisordersRefractive errors cause decreased vision, visual discomfort ("eye strain"), and/or amblyopia.
-
 Recurrent Corneal Erosion
Recurrent Corneal ErosionThe cornea is the clear front windshield of the eye. Erosions occur when the top skin layer of the cornea tear, typically at night-time or when you wake from sleep...
-
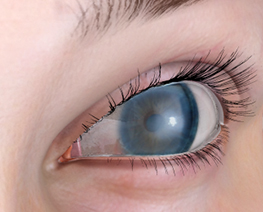 Fuch's Endothelial Dystrophy
Fuch's Endothelial DystrophyFuch's endothelial dystrophy is an inherited degenerative condition of the cornea. The cornea is the clear front windshield of the eye.
-
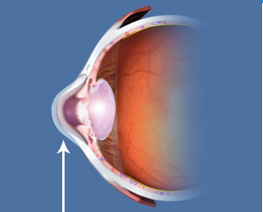 Keratoconus
KeratoconusKeratoconus is a degenerative disorder of the cornea, the clear focusing surface at the front of the eye.
-
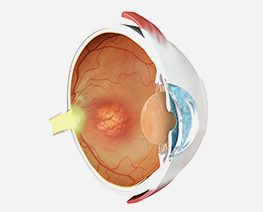 Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic RetinopathyDiabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes and a leading cause of blindness. It occurs when diabetes damages the tiny blood vessels nourishing the retina...
-
 Dry Eyes
Dry EyesA dry eye is one of decreased or deficient tears. It is referred to as Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca.
-
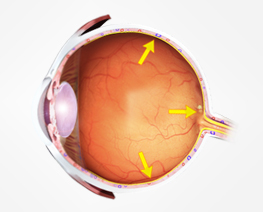 Glaucoma
GlaucomaGlaucoma is a group of diseases that can damage the eye's optic nerve and result in vision loss and blindness.
-
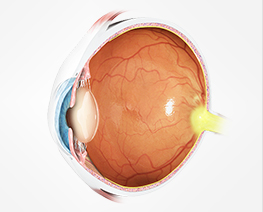 Cataract
CataractCataract surgery has improved dramatically over recent years into one of the safest and most effective operations.
-
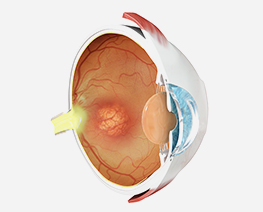 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading to the formation of drusen.
-
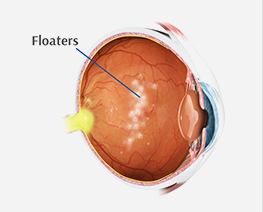 Flashes and Floaters
Flashes and FloatersFloaters are usually seen as spots, cobwebs or strands moving across the vision. They are usually due to particles floating in the vitreous (jelly-like substance that fills the eye).
-
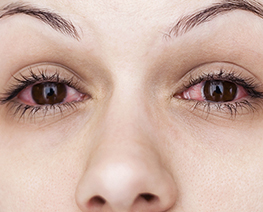 Conjunctivitis
ConjunctivitisConjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva (the surface layer over the white of the eye) causing redness of the eye, swelling of the eyelids and watery or mucous discharge.
-
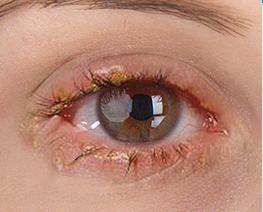 Blepharitis
BlepharitisBlepharitis is a common, chronic problem of the eyelid margin which causes irritation, redness and crusting of the eyelids.
-
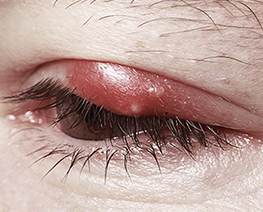 Chalazion in Children
Chalazion in ChildrenWithin the eyelid, there are many meibomian glands that produce oily fluid that forms part of the tears.
-
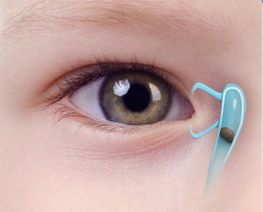 Blocked Tear Ducts in Children
Blocked Tear Ducts in ChildrenTears normally flow into the nose via the tear duct. Sometimes the lower end of the tear duct fails to open at birth.
-
 Adult Strabismus
Adult StrabismusStrabismus or squint is a condition in which the two eyes are not pointing in the same direction.
-
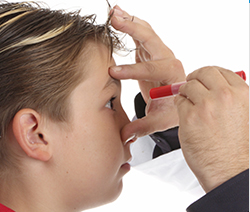 Paediatric Ophthalmology
Paediatric OphthalmologyA squint occurs when the two eyes are not pointing in the same direction. Most commonly, one eye will turn in or out...







